Acupuncture
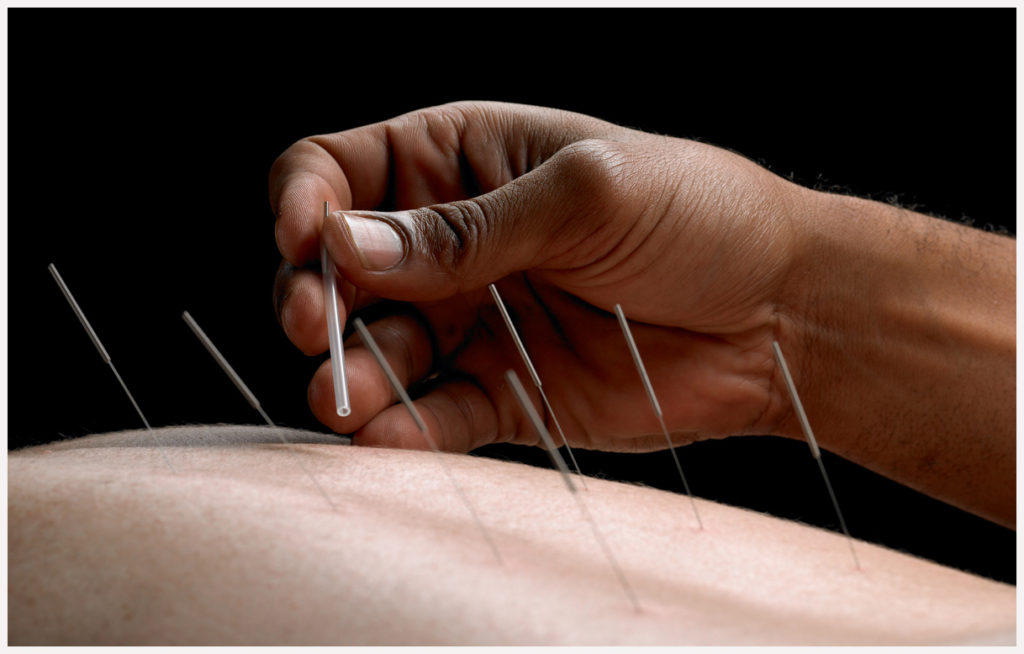
Acupuncture is a Chinese medical system that is more than 3,000 year old. Acupuncture is the process of stimulating specific points on the body to correct imbalances of Qi or Chi (vital energy) in channels that flow up and down the body called meridians. It is believed that when these meridians are in a sate of imbalance pain or disease occurs. The most common technique of stimulation of acupuncture points employs penetration of the skin by stainless steel needles, which are manipulated manually or by electrical stimulation or Moxibustion on or over selected points.
Chinese Herbal Medicine
A system of diagnosis and treatment using medicinal herbs, one of the branches of traditional Chinese medicine. Herbs used range from the nontoxic and rejuvenating, such as ginseng, which are used to support the body’s healing system, to highly toxic ones, such as aconite, used in the treatment of disease.
Cupping
A therapy in which heated glass cups are applied to the skin along the meridians of the body, creating suction as a way of separating adhesion of muscles, stimulating the flow of energy/Qi and encourage the circulation of old stagnant blood to promote healing.
Moxibustion
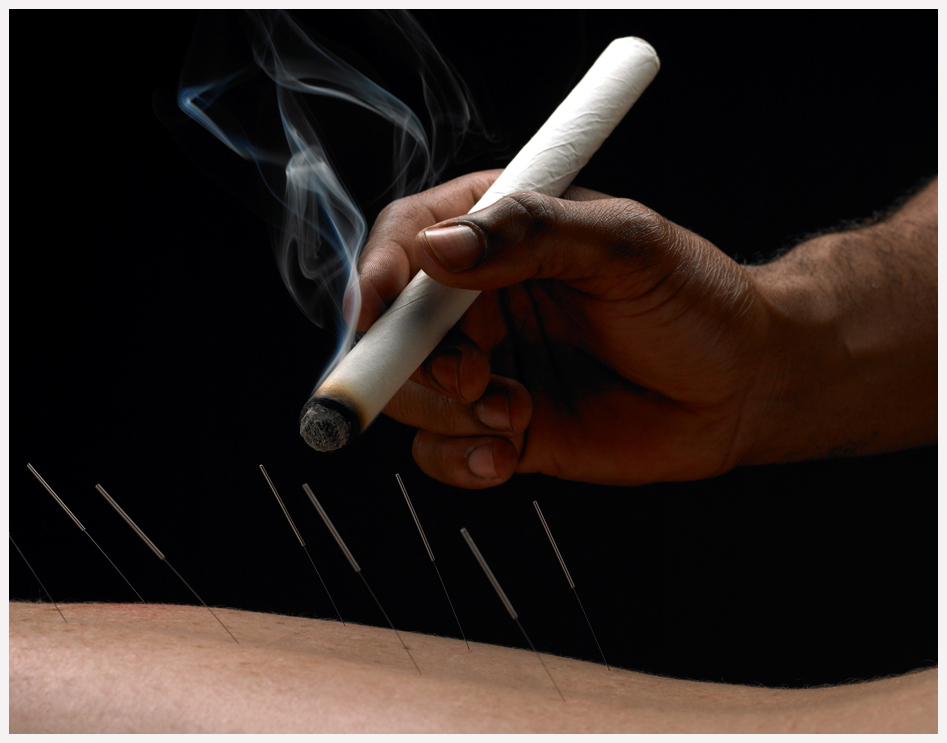
A form of TCM therapy used both as a primary treatment and as an adjunct and synergistic technique to acupuncture. With its ability to penetrate deeply into the skin Artemisia vulgaris (mugwort) has been used as the primary herb for moxa therapy because of the unique ability of its heat to penetrate deeply beneath the skin. In China , moxa therapy is generally taken to mean the therapeutic effect of applying ignited mugwort over affected parts of the body and to acupuncture points.